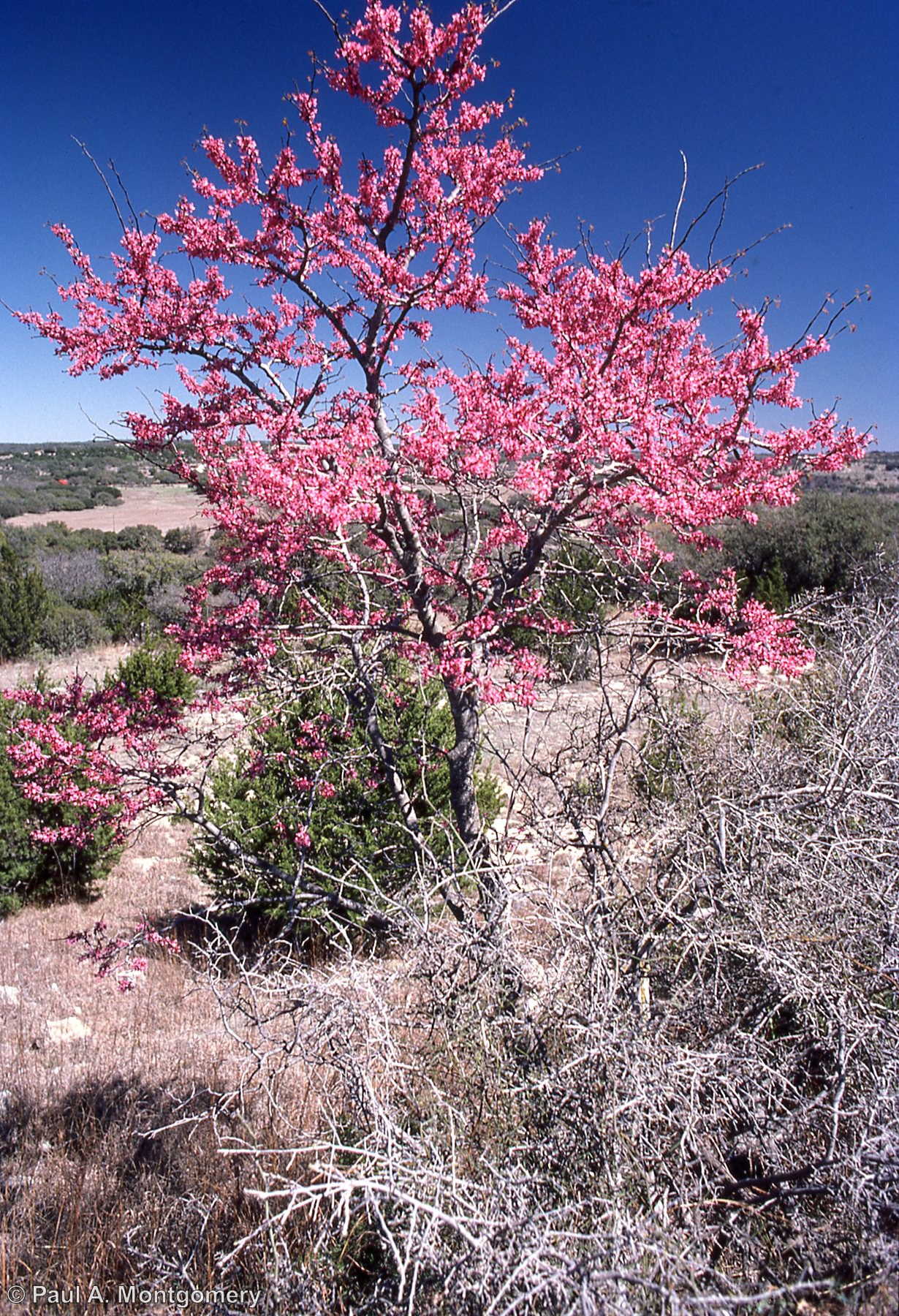
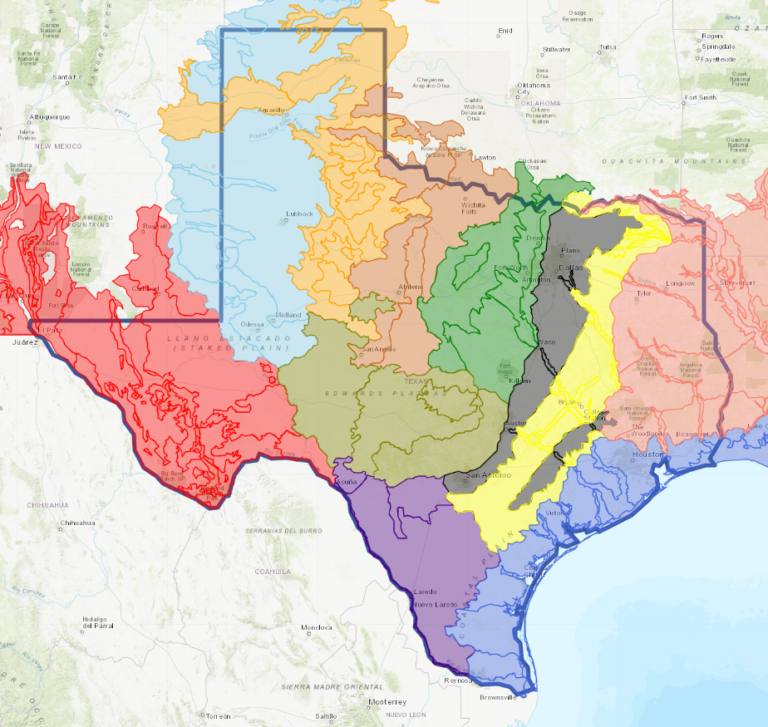
Salado, the location of our Fall 2025 Symposium, lies at the intersection of two ecoregions: the Edwards Plateau (Limestone Cut Plain) and Blackland Prairie (Northern Blackland Prairie).
The Edwards Plateau area is also called the Hill Country; however, this general term covers a much larger area extending farther north. Spring-fed creeks are found throughout the region; deep limestone canyons, rivers, and lakes (reservoirs) are common. Ashe juniper is perhaps the most common woody species found throughout the region. Additional woody species include various species of oak, with live oak (Quercus fusiformis) being the most common. Sycamores (Platanus occidentalis) and bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) border waterways. This area is well known for its spring wildflower displays, though they may be viewed in spring, late summer, and fall, as well. According to Texas Parks and Wildlife, average annual rainfall in the Edwards Plateau ranges from 15 to 34 inches.
The Blackland Prairie extends from the Red River south to San Antonio, bordered on the west by the Edwards Plateau and the Cross Timbers, and on the east by the Post Oak Savannah. Annual rainfall averages 30 to 40 inches, with higher averages to the east. This region is dominated by prairie species. The most common grass species include little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium) and Indian grass (Sorghastrum nutans) in the uplands and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) in the riparian areas and drainages. Common herbaceous flowering plants include salvias, penstemons, and silphiums. This area has suffered greatly from overgrazing and agricultural use. Few intact areas remain, though many of the plants can be found along county roadsides throughout the region.
Our fall Symposium host chapter, the Tonkawa Chapter, includes both of these ecoregions.
Source: Wildflowers of Texas by Michael Eason